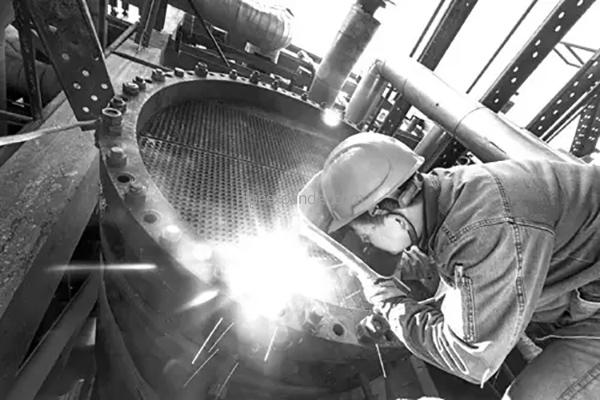
Manufacture of double tube plate heat exchanger
Abstract
The tube sheet processing and strength expansion of double tube sheet heat exchangers are the difficulties and key points in the manufacturing process. During the manufacturing process, the manufacturing process must be strictly followed and the double tube sheet heat exchanger must be processed, manufactured and inspected in combination with the actual manufacturing situation.
1. Double tube sheet structure
Double tube sheet is a newer structural form in heat exchangers. If the two media in the tube side and shell side are mixed, the material will be scrapped or a major accident will occur. This double tube sheet structure is generally used. The structural forms are: one is the inner tube sheet strength expansion, the outer tube sheet expansion + sealing welding; the other is the inner and outer tube sheets are both strength expansion. The two tube sheets are divided into the use of half short section connection and the two tube sheets are directly connected through the fillet weld. Both structures form an intermediate liquid accumulation cavity. The tube sheet connection form of this batch of heat exchangers is: inner tube sheet strength expansion, outer tube sheet expansion + sealing welding.
2. Expansion process evaluation
The biggest difficulty in the heat exchanger manufacturing process is the strength expansion of the inner tube sheet, which must be guaranteed to be 100% qualified after expansion. Generally, the hardness of the tube sheet is required to be about 30HB higher than the hardness of the tube. The tube sheet and the tube of the heat exchanger are made of the same material, which makes it more difficult to expand the strength. Therefore, when ordering the tube sheet and the tube, the hardness is limited respectively. In order to ensure the qualified rate of expansion, the expansion process must be evaluated before the product is expanded to select the appropriate expansion parameters.
Evaluation test steps
(1) Selection of expansion groove size. According to the requirements of the "Capacity Regulations", the groove width is 8mm and the groove depth is 0.5mm. The expansion groove width remains unchanged and the expansion groove depth is changed to 0.6mm.
(2) Make a simulated tube sheet, the material, thickness, drilling diameter, etc. are consistent with the actual product.
(3) Order a hydraulic tube expander according to the size of the tube sheet and the tube and the size of the expansion area.
(4) Preliminarily set a strength expansion parameter value based on previous expansion experience, and conduct expansion tests every 5-10MPa on this value.
(5) After the expansion test is completed, the simulated tube sheet is first subjected to a water pressure test according to the product water pressure test value, and a penetrant developer is sprayed on the tube head end to facilitate observation of water leakage. After the water pressure test is passed, an ammonia leakage test is carried out. For the leaking tube head, the expansion pressure is appropriately increased and the expansion is re-expanded.
(6) The strength expansion test specimen is re-processed, and the strength expansion is carried out according to the determined expansion parameters. The pull-off force and dissection test are carried out on the expanded tube. The pull-off force results are all greater than 4MPa.
Manufacturing Key Points
The manufacturing key points are the concentricity and parallelism of the tube holes of the inner and outer tube sheets, and the key is the concentricity and roughness of the inner tube sheet strength expansion groove and the tube hole.
(I) Processing of inner and outer tube sheets. In order to ensure the concentricity and verticality of the two tube sheets, a high-efficiency CNC drilling machine is used for bottom hole drilling and drilling. The manufacturing process is strictly followed to control the hole diameter and roughness, and spiral or longitudinal scratches are not allowed. The aperture of the outer tube sheet is about 0.1mm larger than that of the inner tube sheet. This is because the distance between the inner and outer tube sheets is small, and the rigidity of the tube between them is very large, making it difficult to make local adjustments. From the expansion test research, it can be seen that the expansion groove of the inner tube sheet directly determines the quality of the strength expansion. If the concentricity of the expansion groove and the tube hole exceeds the tolerance, the shallow side of the expansion groove cannot be expanded under the tensile force of the deep side of the expansion groove, and thus the sealing effect cannot be achieved. If the roughness of the expansion groove exceeds the tolerance, the tube cannot be firmly attached to the groove during the strength expansion, and the sealing is also not tight. Therefore, a special hole and groove boring tool should be used for processing, and chips should be removed in time to ensure tolerance and roughness.
(II) Baffle processing. The concentricity of the baffle hole and the tube sheet hole directly affects whether the tube can be smoothly inserted into the tube hole. Therefore, the processing of the baffle should be grouped by quadrants, and the baffles in a quadrant should be fixed together with straight plates, and the front marks should be made. The ends of the baffle holes should be chamfered to remove burrs. The tolerance range of the baffle aperture should be appropriately adjusted according to the size of the baffle spacing. If the spacing is less than 150mm, the tolerance should be appropriately increased by about 0.3mm.
(III) Pre-assembly of inner and outer tube sheets. Clean the iron filings, oil stains and other foreign objects in the tube holes of the inner and outer tube sheets, overlap the inner and outer tube sheets in the product order, use the positioning pins to position them, and then use the heat exchange tubes to punch holes one by one, and check the concentricity and verticality of the holes of the two tube sheets. If a tube cannot pass through the two tube sheets, rotate one of the tube sheets 180° before trying it out, and make orientation marks and positive and negative marks.
(IV) Tube bundle assembly. Taking the inner tube sheet as the reference, insert the tie rod, spacing tube, baffle, support plate, etc. in turn, and then fix the outer tube sheet and the inner tube sheet together. When inserting the tube, proceed from the inside to the outside, insert a row, and adjust a row of tube heads so that the length extending out of the outer tube sheet is 3-4mm. During the pipe threading process, do not hit the pipe directly with a hammer. Instead, shake the U-shaped pipe slightly up and down, and use a traction tool at the end of the pipe to allow the pipe to pass smoothly into the pipe hole.
(V) The hydraulic expansion of the inner tube sheet is the biggest difficulty in the manufacture of the entire double tube sheet heat exchanger. During strength expansion, the outer tube sheet and the inner tube sheet should be fixed according to the product structure, and the expansion tube lengthening mechanism should be used. Before expansion, the distance from the tube head to the expansion area of the inner tube sheet should be accurately measured, and then the retaining ring should be processed to accurately position it. This distance should be appropriately adjusted according to the actual size of the tube head extending out of the outer tube sheet to prevent expansion from the wrong position. Generally, the two-time expansion method is used: the first expansion is carried out according to the parameter value determined by the expansion process evaluation; the second expansion is carried out according to a slightly higher expansion force than the first expansion. The two-time expansion method or even multiple expansion methods are effective methods for preventing pipe leakage based on manufacturing experience. When expanding, the expansion should be carried out in a certain order to prevent leakage. For example, expand the tubes in the order from top to bottom, from left to right, or according to the layout of the tubes, and mark them until the expansion is completed.
(VI) Welding and expansion of the outer tube sheet. The outer tube sheet and the inner tube sheet can be welded together only after the inner tube sheet expansion inspection is qualified. Argon arc welding is used during the welding, and argon gas is passed into the liquid accumulation cavity for protection, and the interlayer temperature is strictly controlled. The welding of the outer tube sheet head is carried out by an automatic tube sheet sealing welding machine, and generally two wire filling methods are used. During welding, in order to prevent the tube sheet from being deformed due to excessive heat, the alternate row welding method is used. After welding, the tube head is 100% color checked. After welding, the outer tube sheet head is hydraulically expanded. After spot checking the inner diameter of some tube heads, the diameter of the expander is ground to facilitate the smooth penetration of the expander into the tube, and then the tube head is expanded according to the expansion parameters determined by the pull-off force test, and the quality of the expansion of the inner wall of the tube is preliminarily judged by visual inspection. The outer tube sheet adopts the method of welding first and then expanding, mainly to improve the quality of tube head sealing. If expanding is done first, a dead zone is often formed at the tube head, which is not conducive to the flow of gas and causes welding defects.
(VII) Pressure test. The pressure test of the double tube sheet heat exchanger is relatively complicated. First, the shell side water pressure test is carried out. At this time, the outer tube sheet must be removed, and the developer is sprayed on the inner tube sheet to facilitate the inspection of the leakage of the inner tube sheet. After the water pressure test is passed, the shell side is tested for air tightness. After the air tightness test is passed, the inner and outer tube sheets and the outer tube sheet tube head are welded together to make the liquid accumulation cavity a closed cavity. The liquid accumulation cavity is subjected to water pressure test and air tightness test. Since the volume of the liquid accumulation cavity is very small, a tooling buffer tank is made during the pressure test, which is convenient for observing the pressure change more stably during the pressure test. After the pressure test is completed, an ammonia permeation test is carried out according to the drawing, and a test paper is pasted at the drainage hole of the liquid accumulation cavity, and the reagent is sprayed at the tube head. The test paper and the reagent do not change color and are qualified. Finally, the pipe is subjected to water pressure test and air tightness test. For this type of product, the jacket is also subjected to water pressure test.

 German
German Spanish
Spanish French
French Italian
Italian Portuguese
Portuguese Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Russian
Russian Indonesian
Indonesian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Send Email
Send Email 008617372818528
008617372818528